Promises in LWC
Hello folks!
What is JavaScript Promise? How does it work with Lightning Web Component? What is the better choice to resolve promises in LWC?
Well, let’s get down to the details.
Check also Then vs Async Await in LWC.
Introduction
Javascript is a single threaded.
- What does it mean?
Only one operation at a time. Code is executed line by line.

- What is the problem with this approach?
UI (your browser window) can freeze at the time of code execution. Is really bad from the user experience perspective.
- How we can resolve it?
Asynchronous JavaScript!
You will get a Promise that code will be done some time in the future. You don’t know when, but you will be able to detect it (then or await).
Promise
Promise lets asynchronous methods return values like synchronous methods: instead of immediately returning the final value, the asynchronous method returns a promise to supply the value at some point in the future. ~ MDN
A Promise is in one of these states:
- pending: initial state, neither fulfilled nor rejected.
- fulfilled: meaning that the operation was completed successfully.
- rejected: meaning that the operation failed.
Each state fires an associated handler.
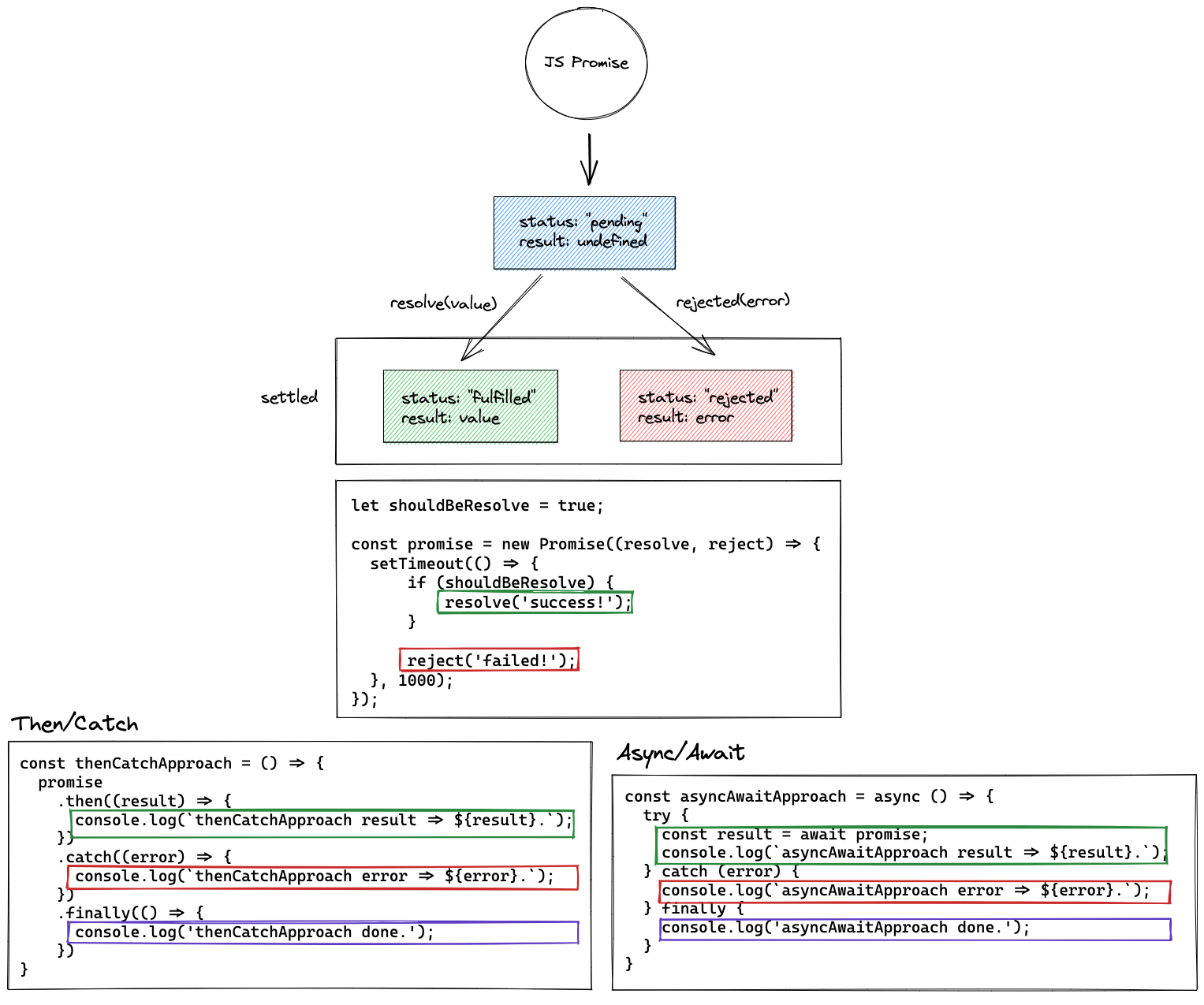
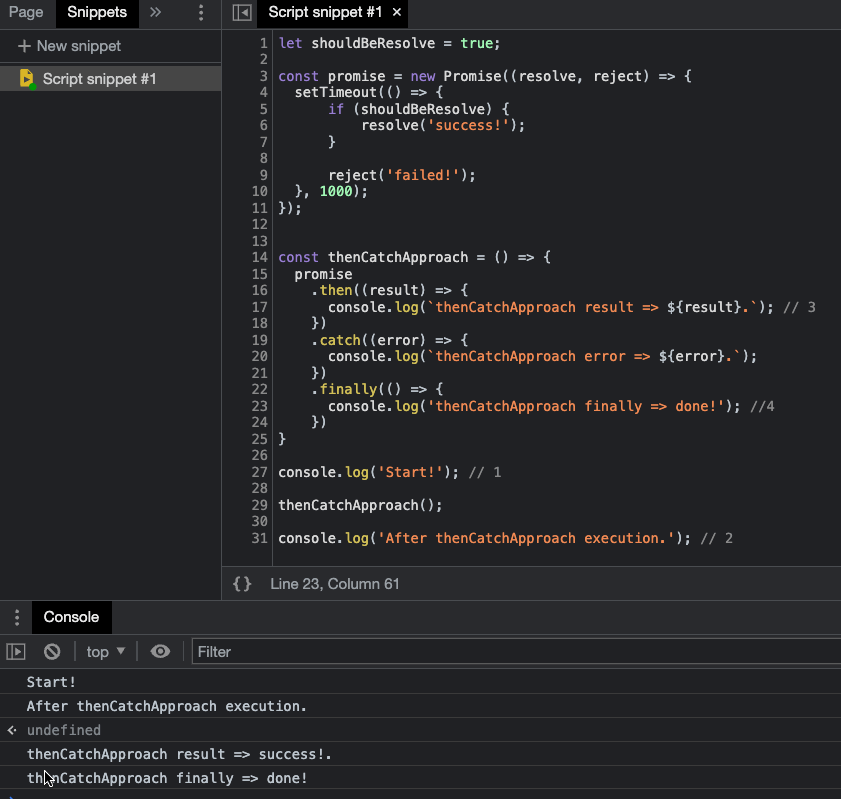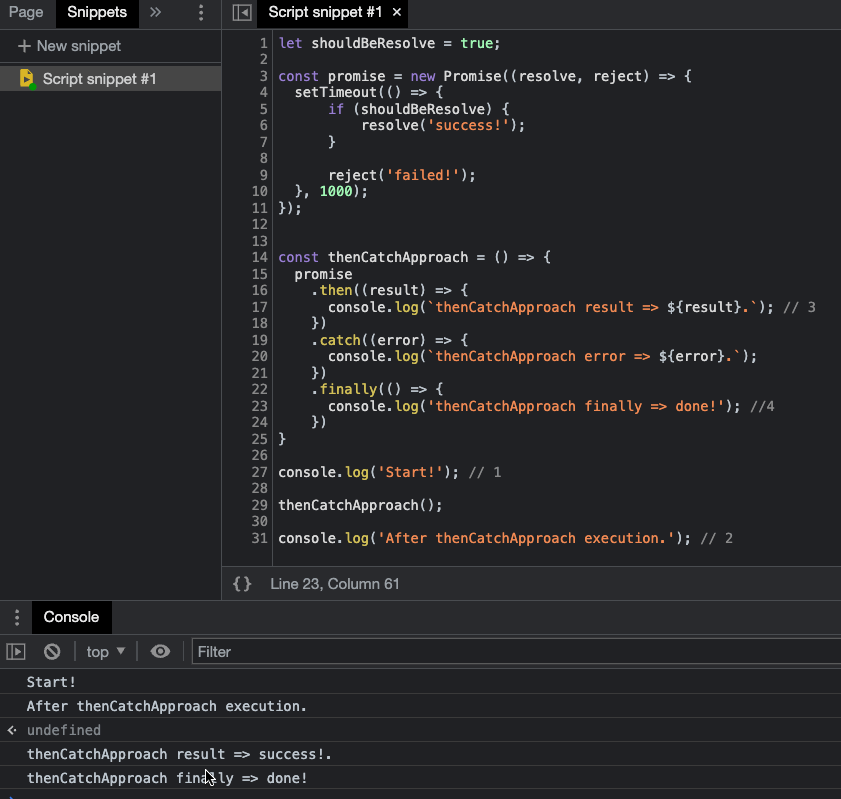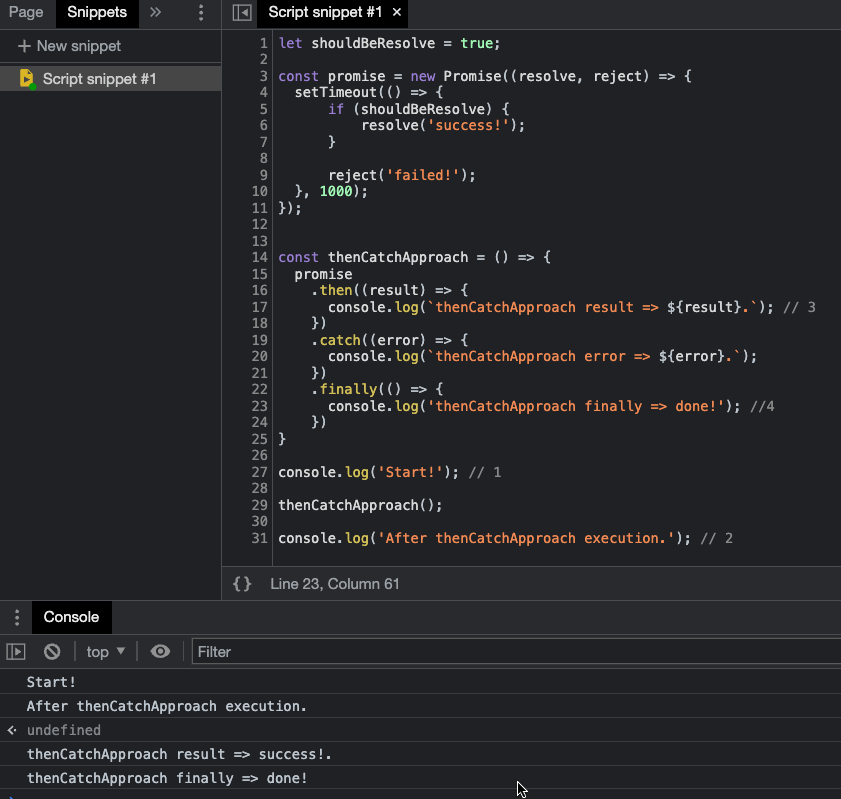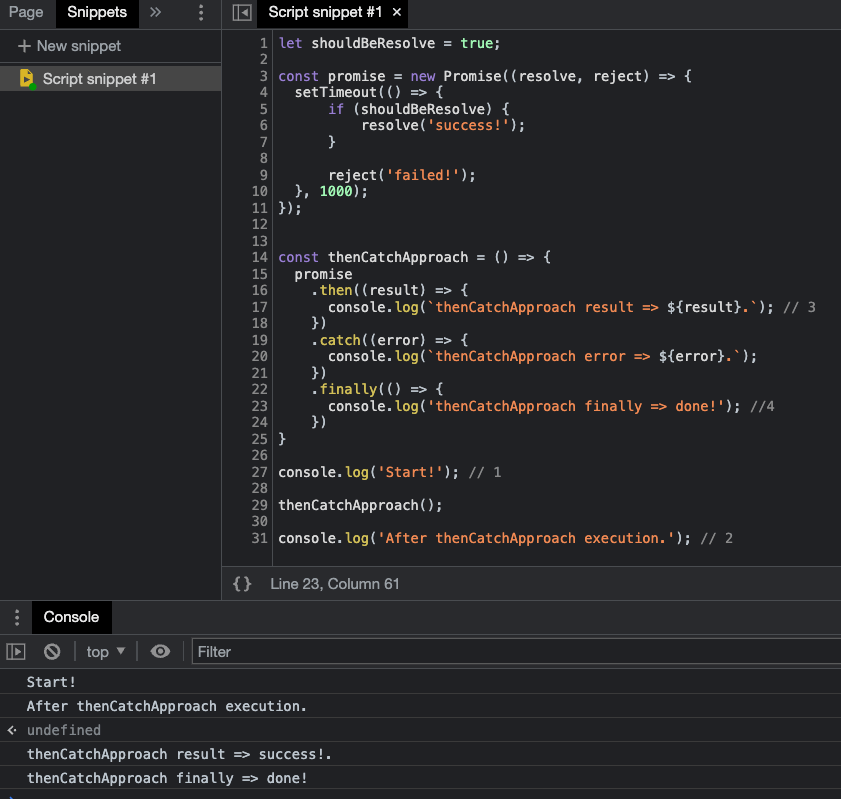
Code
let shouldBeResolve = true; const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { if (shouldBeResolve) { resolve('success!'); } reject('failed!'); }, 1000); }); // then/catch const thenCatchApproach = () => { promise .then((result) => { console.log(`thenCatchApproach result => ${result}.`); }) .catch((error) => { console.log(`thenCatchApproach error => ${error}.`); }) .finally(() => { console.log('thenCatchApproach done.'); }) } // async/await const asyncAwaitApproach = async () => { try { const result = await promise; console.log(`asyncAwaitApproach result => ${result}.`); } catch (error) { console.error(error); console.log(`asyncAwaitApproach error => ${error}.`); } finally { console.log('asyncAwaitApproach done.'); } } // success shouldBeResolve = true; thenCatchApproach(); asyncAwaitApproach(); // error // shouldBeResolve = false; // thenCatchApproach(); // asyncAwaitApproach();
Promises in LWC
All apex functions return a promise.
import apexMethodName from '@salesforce/apex/Namespace.Classname.apexMethodReference';
The imported function returns a promise. ~ Salesforce
We can resolve the apex method in three ways:
@wire- Then/Catch
- Async/Await
Wire
When to use?
- Result can be cached. To use
@wireapex method needs to be marked as(Cacheable=true). @wireis great to read the data. DML (insert, update, delete) operations are not supported.
Code
- Wire an Apex Method to a Property
import apexMethodName from '@salesforce/apex/Namespace.Classname.apexMethodReference'; @wire(apexMethodName, { apexMethodParams }) property;
- Wire an Apex Method to a Function
import apexMethodName from '@salesforce/apex/Namespace.Classname.apexMethodReference'; @wire(apexMethodName, { apexMethodParams }) wiredFunction({ error, data }) { if (data) { console.log(data); } else if (error) { console.error(error); } }
Then/Catch
When to use?
- Operation on the database is needed (DMLs – insert, update, delete).
- Data cannot be cached.
- Apex should be invoked after user action (e.g. onclick).
Code
import apexMethodName from '@salesforce/apex/Namespace.Classname.apexMethodReference'; apexMethodName .then(result => { console.log(result); }) .catch(error => { console.error(error); }) .finally(() => { console.log('done.'); //good place to hide spinner })
Async/Await
When to use?
- Operation on the database is needed (DMLs – insert, update, delete).
- Data cannot be cached.
- Apex should be invoked after user action (e.g. onclick).
- The code should behave as synchronous.
Code
import apexMethodName from '@salesforce/apex/Namespace.Classname.apexMethodReference'; try { let result = await apexMethodName; } catch (error) { console.error(error); } finally { console.log('done.'); //good place to hide spinner }
- Chain Execution
import { LightningElement } from 'lwc'; import apexMethod1 from '@salesforce/apex/ClassName.apexMethod1'; import apexMethod2 from '@salesforce/apex/ClassName.apexMethod2'; import apexMethod3 from '@salesforce/apex/ClassName.apexMethod3'; export default class LwcPromise extends LightningElement { connectedCallback() { this.invokeApexMethods(); } async invokeApexMethods() { try { const result1 = await apexMethod1(); const result2 = await apexMethod2({ param: result1 }); const result3 = await apexMethod3({ param: result2 }); } catch(error) { console.error(error); } finally { console.log('Finally Block'); } } }
Consideration
- Async function always returns a promise.
async function myAsyncFunction() { return 'hello async promise!'; } myAsyncFunction().then(result => console.log(result)); //hello async promise! //or await myAsyncFunction(); //hello async promise!
- Await can be used only in a method signed as
async.
If you have any questions feel free to ask in the comment section below. 🙂
Recommended post: Then vs Async Await in LWC
Was it helpful? Check out our other great posts here.
